

This phase may begin 4-6 hours after ingestion in a young infant or 24 hours or more after ingestion in an adolescent or adult. Phase 3 includes dehydration, hypokalemia, and progressive metabolic acidosis. This phase may begin within hours and may last 12-24 hours. In phase 2, paradoxic aciduria in the presence of continued respiratory alkalosis occurs when sufficient potassium has been lost from the kidneys. Both potassium and sodium bicarbonate are excreted in the urine. Phase 1 of the toxicity is characterized by hyperventilation resulting from direct respiratory center stimulation, leading to respiratory alkalosis and compensatory alkaluria.

Thrombosis is also prevented with a low dose of Aspirin.

Many people are using Aspirin as an anti-inflammatory agent to treat soft tissue and inflammation in the joints. Therapeutic uses of salicylates are the following:Īcetylsalicylic acid is colorless or white in a crystalline, powder, or granular form. The chemical used in this drug is odorless and is soluble in water. They are available for ingestion as tablets, capsules, and liquids.
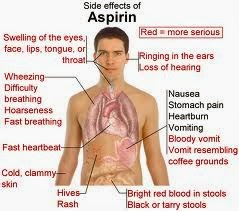
These medications possess anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic properties. Salicylates are agents found in hundreds of over-the-counter (OTC) medications and in numerous prescription drugs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
